pure axial compression material test data graph|Compression Test : company The compression stress-strain curve is a fundamental graph used in civil engineering for analyzing the behavior of structural materials like concrete, steel, soil and more when subjected to compressive loading forces. webICQ New: Se vale tudo
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 29 de dez. de 2016 · 4. Seus seguidores são chamados de "gafanhotos" e "libélulas". Aos 28 anos de idade, Zangado é mais velho do que seu público (e do que boa parte dos .
The goal of a compression test is to determine the behavior or response of a material while it experiences a compressive load by measuring fundamental variables, such as, strain, stress, .The compression stress-strain curve is a fundamental graph used in civil engineering for analyzing the behavior of structural materials like concrete, steel, soil and more when subjected to compressive loading forces.Using the data acquired during a tensile test, a stress-strain curve can be produced. In this post, we will create a stress-strain curve (a plot) from a set of tensile test data of a steel 1045 sample and an aluminum 6061 sample.
The goal of compression testing is to ascertain how a material responds to a compressive load. This is essential when determining if a material is appropriate for a given task, such as developing structural elements or assuring the quality .
Interpreting Compression Stress
The test specimens were placed at the centre of the end plates, and a UTM of 1000 kN capacity was used to apply pure vertical axial compression loading. The test load was continuously applied under a displacement control method at a rate of 0.2 mm/s till the failure of the test specimen. The axial load (P) versus deformation capacity (δ) of .and computational methods for a rectangular filleted bar in tension and in pure bending. Text Figure A-15-5 provides tensile test results for the bar in simple tension while Figure T3-13-1 shows TEXT FIGURE A-15-5: . material, is subjected to a static axial load. Find: The critical section of the bar. Solution Methodology:Figure 11.5: Axial stress vs axial strain graph Report. Use the template provided to prepare your lab report for this experiment. Your report should include the following: Objective of the test; Applications of the test; Apparatus used; Test procedures (optional) Analysis of test results – Complete the table provided and show one sample .for ductile materials, asymmetric response in tension-compression for brittle materials with higher strength in compression, no plastic yielding, etc. Consider the case of a ductile material. For this simple stress state, the material yields plastically when: 11 = y 5.2 Plastic yielding under multi-axial stress states Readings: BC 2.3 117
Commonly, not all three or even two types of test data are available. Figure 9 to Figure 15 show the consequences of using different hyperelastic forms with only the uniaxial tension data. The following cases are analyzed: Polynomial form with N = 1 (Mooney-Rivlin form) and N = 2.. Reduced polynomial form with N = 1 (neo-Hookean form) and N = 3 (Yeoh form).If the material yield stress is the same in tension and compression (κ=1)then the Burzynski criterion reduces to the von Mises criterion at impending failure: σB(@κ=1)= @0+ √4σM2 A/2=σM=kt When the material yield stress is the same in tension and compression (𝜅=1) then the Burzynski criterion reduces to the von Mises criterion.
Compression testing is one of the most fundamental types of mechanical testing, alongside tensile and flexion tests. Compression tests are used to determine a material’s behavior under applied crushing loads, and are typically conducted by applying compressive pressure to a test specimen (usually of either a cuboid or cylindrical geometry) using platens or specialized .In-Plane Shear Test: Often used for composite materials, this test involves applying a force parallel to the plane of the material until it fails. V-Notched Rail Shear Test: This is a modification of the rail shear test where a V-notch is introduced to the specimen to increase shear stress concentration. It’s often used for testing composite .
The properties of the uniaxial test will be discussed first, before considering triaxial and other multiaxial loading cases. In its simplest form, the uniaxial compression test is conducted by taking a right cylinder of intact rock, loading it along its axis and recording the displacement produced as the force is increased. 2.2. Materials. Before evaluating the strength of concrete brick prism, material test of each component, brick and mortar, was performed. The test protocol of compressive strength of standard concrete brick (190 × 90 × 57 mm) followed KS F404 [].The test result shows that the average compressive strength of 11 specimens was 8.23 MPa and the standard .
In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain.It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing).These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's .tension, compression or torsion test. A material may exhibit di erent properties depending on the type of load applied. In this test, the applied load is compressive in nature. When a material undergoes uniaxial compression, the atoms or molecules tend to come close together in the direction of the applied force.Strain is a unitless measure of how much an object gets bigger or smaller from an applied load.Normal strain occurs when the elongation of an object is in response to a normal stress (i.e. perpendicular to a surface), and is denoted by the Greek letter epsilon.A positive value corresponds to a tensile strain, while negative is compressive.Shear strain occurs when the .
The axial (ε c, A) and the lateral (ε c, L) strains were measured with strain gauges placed in the middle of the test prism (Figure 2b). Under axial compression, the concrete exhibited an almost linear response up to around .
Answer to 5 A series of triaxial compression tests on specimens. 5 A series of triaxial compression tests on specimens of a slate gave the following results: Confining Peak axial Angle between stress cleavage and pressure の(MPa) . where \(\epsilon_L\)is the lateral strain and \(\epsilon_A\) is the axial strain. Note the negative sign which signifies a decrease in length. The Poisson’s ratio is typically around 0.3 for metals, 0.5 for rubber, 0.4-0.5 for .Design value of acting axial force A c . Total area of pure concrete section f cd . Design value of the compressive strength of concrete Compressive Stress in Steel . The concrete shrinkage under axial compression is limited to ε c2 in the case of the σ-ε parabola-rectangle diagram. By static friction of concrete and steel, the .
The graph on the right then shows true stress-true strain plots, and nominal stress-nominal strain plots, while the schematic on the left shows the changing shape of the sample (viewed from one side). Note that the elastic strains are not shown on this plot, so nothing happens until the applied stress reaches the yield stress.1028 Mechanical Engineering Design Table A–15 Charts of Theoretical Stress-Concentration Factors K* t (Continued) Figure A–15–7 Round shaft with shoulder fillet in tension. σ0 = F/A, where A = πd2/4. Figure A–15–8The variation of axial stress versus axial strain in compression and extension can be seen in Figure 2.The stress-strain curve is hyperbolic, which is a characteristic of the Hardening Soil material model; as the axial displacement increases, the axial stress increases hyperbolically, and then asymptotically matches the corresponding failure stress given in the Table 1.Figure 1, Advanced material models need multiple strain conditions for safe calibration. This data set contains tensile, shear, and in-plane compression data. Figure 2, Plastic tensile test with an axial extensometer mounted to the specimen. to generate experimental data that may be used to calibrate the material constants in material
(1)The test data is derived from domestic and international literature, involving different concrete strength indicators. For the convenience of comparative analysis, this paper unifies the different strength indicators into axial compressive strength f ck: when the compressive strength of the cylinder, f c ’ <=40MP, the compressive strength of the cube, f cu,k =1.25*f c ’; .
The pre-determined lateral stresses and the corresponding axial stresses on failure are presented in Table 1: Table 1: Triaxial test results data example. The results are plotted with the best-fit M-C and H-B envelopes in Figure 3. Figure 3: Principal stress plot based on laboratory data and best-fit envelopes of M-C and H-B criteria.
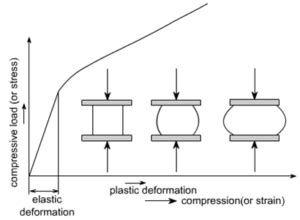
A compression test is one of the most fundamental mechanical tests that can be performed on a material, product, or component. Our compression test machines measure characteristics such as yield strength, ultimate strength, modulus of elasticity, and stress-strain. Each compression test machine is configured to your testing needs by our application engineers with the correct .This restricts the applicability of this derivation to linear elastic materials. Hence the axial normal stress, like the strain, increases linearly from zero at the neutral axis to a maximum at the outer surfaces of the beam. . Consider a beam loaded in axial compression and pinned at both ends as shown in Figure 6. Now let the beam be made .Figure 2.5 shows the schematic setup for applying axial compression loads to the test pile using a hydraulic jack acting against a platform. The platform was composed of steel sheets and concrete boxes with a total weight of 500 kN supported by upper cross H beams. The reaction beam or test beam was support by lower cross H beams supported by a concrete box that .
refractometer sugar salt
refractometer sugar scale
Compression Test
Axial Compressive Load

Skokka. Rio de Janeiro - RJ. 14/02/2017 às 16:52. ID: 24258.
pure axial compression material test data graph|Compression Test